Premium Photoshop Editing On Every Scan.
49¢ most slides. Expert Slide and Photo
Scanning Since 2002.
4,000 ppi Extra High Res Scanning.
We can make PRINTS from your Slides.
Personally Processed with care in Wisconsin.
Louisiana 35mm Slide, Photo & Film Scanning

All scanning companies will NOT give you the same results — click to see proof.
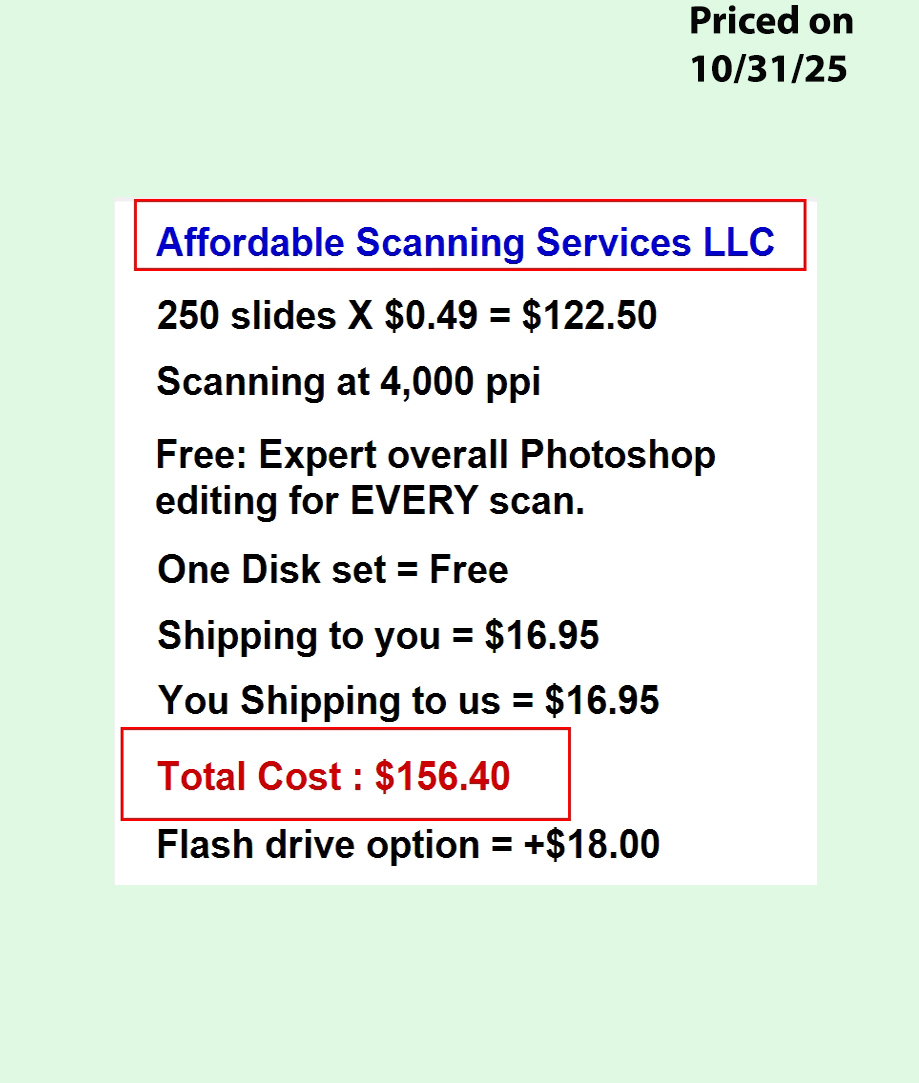
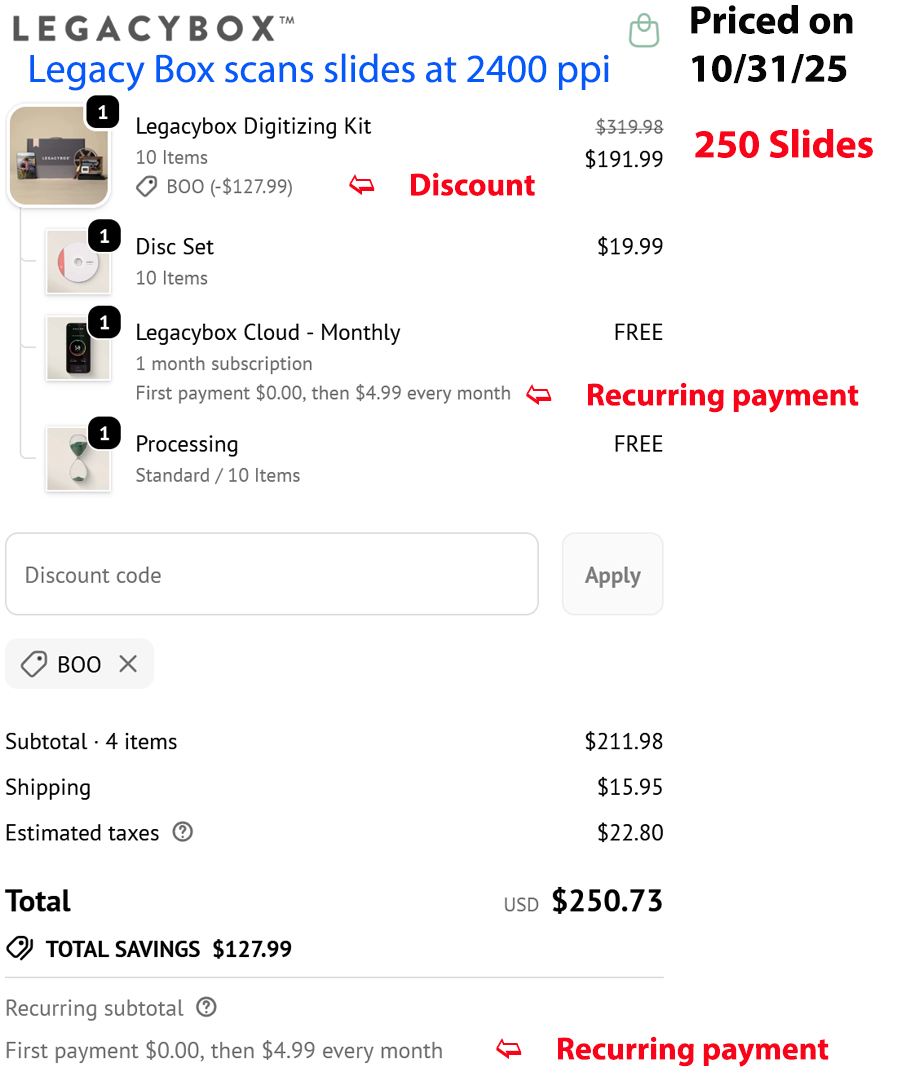
We'll be upfront: we don't have a walk-in location in Louisiana. Most customers ship their projects to us because they want expert results at a fair price and there aren't many strong in-state options. Our before/after images and price comparisons show exactly what to expect.
At Affordable Scanning Services LLC, your job never leaves our Wisconsin offices until it ships back to you. We treat your family photos as if they were our own—handled carefully, edited by hand, and scanned at high resolution.
Since 2002 we've helped customers across New Orleans, Baton Rouge, Shreveport, Lafayette, Lake Charles, Kenner, Bossier City, Monroe, Alexandria, and New Iberia—plus the rest of the U.S. and Canada—by mail. If you have questions, we'll answer quickly and plainly.
"The French explorer Robert Cavelier de La Salle named the region Louisiana to honor France's King Louis XIV in 1682. The first permanent settlement, Fort Maurepas, was founded by Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville in 1699… The Louisiana Territory, purchased for less than 3 cents an acre, doubled the size of the United States literally overnight."
From https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Louisiana

 Home
Home Order Forms
Order Forms